Representation of a space in which planning can be performed. Topology specific sampling, interpolation and distance are defined. More...
#include <ompl/base/StateSpace.h>
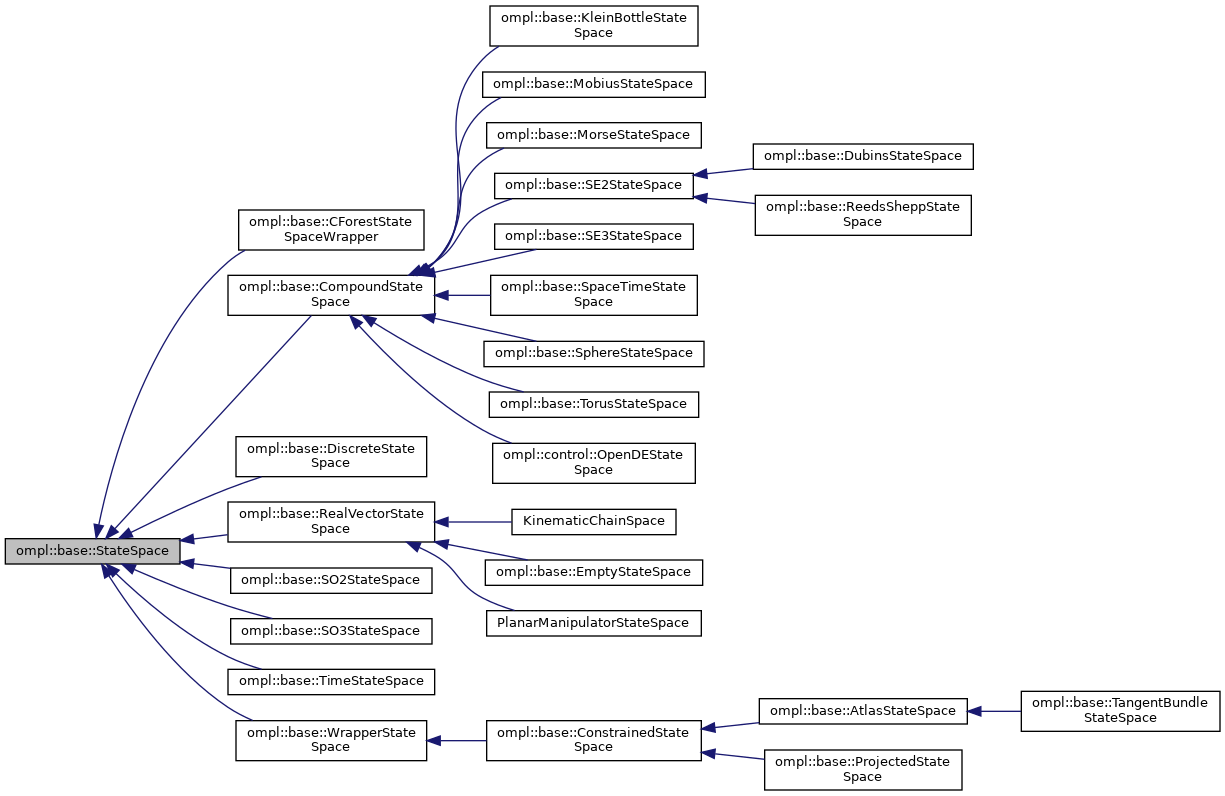
Classes | |
| struct | SubstateLocation |
| Representation of the address of a substate in a state. This structure stores the indexing information needed to access a particular substate of a state. More... | |
| struct | ValueLocation |
| Representation of the address of a value in a state. This structure stores the indexing information needed to access elements of a state (no pointer values are stored) More... | |
Public Types | |
| enum | SanityChecks { STATESPACE_DISTANCE_DIFFERENT_STATES = (1 << 1), STATESPACE_DISTANCE_SYMMETRIC = (1 << 2), STATESPACE_INTERPOLATION = (1 << 3), STATESPACE_TRIANGLE_INEQUALITY = (1 << 4), STATESPACE_DISTANCE_BOUND = (1 << 5), STATESPACE_RESPECT_BOUNDS = (1 << 6), STATESPACE_ENFORCE_BOUNDS_NO_OP = (1 << 7), STATESPACE_SERIALIZATION = (1 << 8) } |
| Flags to use in a bit mask for state space sanity checks. Some basic checks do not have flags associated (they are always executed; for example, whether copyState() works as expected) More... | |
| using | StateType = ompl::base::State |
| Define the type of state allocated by this space. | |
Public Member Functions | |
| StateSpace (const StateSpace &)=delete | |
| StateSpace & | operator= (const StateSpace &)=delete |
| StateSpace () | |
| Constructor. Assigns a unique name to the space. | |
| template<class T > | |
| T * | as () |
| Cast this instance to a desired type. More... | |
| template<class T > | |
| const T * | as () const |
| Cast this instance to a desired type. More... | |
| virtual void | setup () |
| Perform final setup steps. This function is automatically called by the SpaceInformation. If any default projections are to be registered, this call will set them and call their setup() functions. It is safe to call this function multiple times. At a subsequent call, projections that have been previously user configured are not re-instantiated, but their setup() method is still called. | |
Generic functionality for state spaces | |
| virtual bool | isCompound () const |
| Check if the state space is compound. | |
| virtual bool | isDiscrete () const |
| Check if the set of states is discrete. More... | |
| virtual bool | isHybrid () const |
| Check if this is a hybrid state space (i.e., both discrete and continuous components exist) | |
| virtual bool | isMetricSpace () const |
| Return true if the distance function associated with the space is a metric. | |
| virtual bool | hasSymmetricDistance () const |
| Check if the distance function on this state space is symmetric, i.e. distance(s1,s2) = distance(s2,s1). Default implementation returns true. | |
| virtual bool | hasSymmetricInterpolate () const |
| Check if the interpolation function on this state space is symmetric, i.e. interpolate(from, to, t, state) = interpolate(to, from, 1-t, state). Default implementation returns true. | |
| const std::string & | getName () const |
| Get the name of the state space. | |
| void | setName (const std::string &name) |
| Set the name of the state space. | |
| int | getType () const |
| Get the type of the state space. The type can be used to verify whether two space instances are of the same type (e.g., SO2) | |
| bool | includes (const StateSpacePtr &other) const |
| Return true if other is a space included (perhaps equal, perhaps a subspace) in this one. | |
| bool | includes (const StateSpace *other) const |
| Return true if other is a space included (perhaps equal, perhaps a subspace) in this one. | |
| bool | covers (const StateSpacePtr &other) const |
| Return true if other is a space that is either included (perhaps equal, perhaps a subspace) in this one, or all of its subspaces are included in this one. | |
| bool | covers (const StateSpace *other) const |
| Return true if other is a space that is either included (perhaps equal, perhaps a subspace) in this one, or all of its subspaces are included in this one. | |
| ParamSet & | params () |
| Get the parameters for this space. | |
| const ParamSet & | params () const |
| Get the parameters for this space. | |
| virtual double | getLongestValidSegmentFraction () const |
| When performing discrete validation of motions, the length of the longest segment that does not require state validation needs to be specified. This function returns this length, for this state space, as a fraction of the space's maximum extent. | |
| virtual void | setLongestValidSegmentFraction (double segmentFraction) |
| When performing discrete validation of motions, the length of the longest segment that does not require state validation needs to be specified. This function sets this length as a fraction of the space's maximum extent. More... | |
| virtual unsigned int | validSegmentCount (const State *state1, const State *state2) const |
| Count how many segments of the "longest valid length" fit on the motion from state1 to state2. | |
| virtual void | setValidSegmentCountFactor (unsigned int factor) |
| Set factor to be the value to multiply the return value of validSegmentCount(). By default, this value is 1. The higher the value, the smaller the size of the segments considered valid. The effect of this function is immediate (setup() does not need to be called). | |
| virtual unsigned int | getValidSegmentCountFactor () const |
| Get the value used to multiply the return value of validSegmentCount(). | |
| virtual double | getLongestValidSegmentLength () const |
| Get the longest valid segment at the time setup() was called. | |
| virtual void | computeSignature (std::vector< int > &signature) const |
| Compute an array of ints that uniquely identifies the structure of the state space. The first element of the signature is the number of integers that follow. | |
Functionality specific to state spaces (to be implemented by derived state spaces) | |
| virtual unsigned int | getDimension () const =0 |
| Get the dimension of the space (not the dimension of the surrounding ambient space) | |
| virtual double | getMaximumExtent () const =0 |
| Get the maximum value a call to distance() can return (or an upper bound). For unbounded state spaces, this function can return infinity. More... | |
| virtual double | getMeasure () const =0 |
| Get a measure of the space (this can be thought of as a generalization of volume) | |
| virtual void | enforceBounds (State *state) const =0 |
| Bring the state within the bounds of the state space. For unbounded spaces this function can be a no-op. | |
| virtual bool | satisfiesBounds (const State *state) const =0 |
| Check if a state is inside the bounding box. For unbounded spaces this function can always return true. | |
| virtual void | copyState (State *destination, const State *source) const =0 |
| Copy a state to another. The memory of source and destination should NOT overlap. More... | |
| State * | cloneState (const State *source) const |
| Clone a state. | |
| virtual double | distance (const State *state1, const State *state2) const =0 |
| Computes distance between two states. This function satisfies the properties of a metric if isMetricSpace() is true, and its return value will always be between 0 and getMaximumExtent() | |
| virtual unsigned int | getSerializationLength () const |
| Get the number of chars in the serialization of a state in this space. | |
| virtual void | serialize (void *serialization, const State *state) const |
| Write the binary representation of state to serialization. | |
| virtual void | deserialize (State *state, const void *serialization) const |
| Read the binary representation of a state from serialization and write it to state. | |
| virtual bool | equalStates (const State *state1, const State *state2) const =0 |
| Checks whether two states are equal. | |
| virtual void | interpolate (const State *from, const State *to, double t, State *state) const =0 |
| Computes the state that lies at time t in [0, 1] on the segment that connects from state to to state. The memory location of state is not required to be different from the memory of either from or to. | |
| virtual StateSamplerPtr | allocDefaultStateSampler () const =0 |
| Allocate an instance of the default uniform state sampler for this space. | |
| virtual StateSamplerPtr | allocStateSampler () const |
| Allocate an instance of the state sampler for this space. This sampler will be allocated with the sampler allocator that was previously specified by setStateSamplerAllocator() or, if no sampler allocator was specified, allocDefaultStateSampler() is called. | |
| void | setStateSamplerAllocator (const StateSamplerAllocator &ssa) |
| Set the sampler allocator to use. | |
| void | clearStateSamplerAllocator () |
| Clear the state sampler allocator (reset to default) | |
| virtual State * | allocState () const =0 |
| Allocate a state that can store a point in the described space. | |
| virtual void | freeState (State *state) const =0 |
| Free the memory of the allocated state. | |
Functionality specific to accessing real values in a state | |
| virtual double * | getValueAddressAtIndex (State *state, unsigned int index) const |
| Many states contain a number of double values. This function provides a means to get the memory address of a double value from state state located at position index. The first double value is returned for index = 0. If index is too large (does not point to any double values in the state), the return value is nullptr. More... | |
| virtual const double * | getValueAddressAtIndex (const State *state, unsigned int index) const |
| Const variant of the same function as above;. | |
| virtual const std::vector< ValueLocation > & | getValueLocations () const |
| Get the locations of values of type double contained in a state from this space. The order of the values is consistent with getValueAddressAtIndex(). The setup() function must have been previously called. | |
| virtual const std::map< std::string, ValueLocation > & | getValueLocationsByName () const |
| Get the named locations of values of type double contained in a state from this space. The setup() function must have been previously called. | |
| virtual double * | getValueAddressAtLocation (State *state, const ValueLocation &loc) const |
| Get a pointer to the double value in state that loc points to. | |
| virtual const double * | getValueAddressAtLocation (const State *state, const ValueLocation &loc) const |
| Const variant of the same function as above;. | |
| virtual double * | getValueAddressAtName (State *state, const std::string &name) const |
| Get a pointer to the double value in state that name points to. | |
| virtual const double * | getValueAddressAtName (const State *state, const std::string &name) const |
| Const variant of the same function as above;. | |
| virtual void | copyToReals (std::vector< double > &reals, const State *source) const |
| Copy all the real values from a state source to the array reals using getValueAddressAtLocation() | |
| virtual void | copyFromReals (State *destination, const std::vector< double > &reals) const |
| Copy the values from reals to the state destination using getValueAddressAtLocation() | |
Management of projections from this state space to Euclidean spaces | |
| void | registerProjection (const std::string &name, const ProjectionEvaluatorPtr &projection) |
| Register a projection for this state space under a specified name. | |
| void | registerDefaultProjection (const ProjectionEvaluatorPtr &projection) |
| Register the default projection for this state space. | |
| virtual void | registerProjections () |
| Register the projections for this state space. Usually, this is at least the default projection. These are implicit projections, set by the implementation of the state space. This is called by setup(). | |
| ProjectionEvaluatorPtr | getProjection (const std::string &name) const |
| Get the projection registered under a specific name. | |
| ProjectionEvaluatorPtr | getDefaultProjection () const |
| Get the default projection. | |
| bool | hasProjection (const std::string &name) const |
| Check if a projection with a specified name is available. | |
| bool | hasDefaultProjection () const |
| Check if a default projection is available. | |
| const std::map< std::string, ProjectionEvaluatorPtr > & | getRegisteredProjections () const |
| Get all the registered projections. | |
Operations with substates | |
| StateSamplerPtr | allocSubspaceStateSampler (const StateSpacePtr &subspace) const |
| Allocate a sampler that actually samples only components that are part of subspace. | |
| virtual StateSamplerPtr | allocSubspaceStateSampler (const StateSpace *subspace) const |
| Allocate a sampler that actually samples only components that are part of subspace. | |
| State * | getSubstateAtLocation (State *state, const SubstateLocation &loc) const |
| Get the substate of state that is pointed to by loc. | |
| const State * | getSubstateAtLocation (const State *state, const SubstateLocation &loc) const |
| Get the substate of state that is pointed to by loc. | |
| const std::map< std::string, SubstateLocation > & | getSubstateLocationsByName () const |
| Get the list of known substate locations (keys of the map corrspond to names of subspaces) | |
| void | getCommonSubspaces (const StateSpacePtr &other, std::vector< std::string > &subspaces) const |
| Get the set of subspaces that this space and other have in common. The computed list of subspaces does not contain spaces that cover each other, even though they may be common, as that is redundant information. | |
| void | getCommonSubspaces (const StateSpace *other, std::vector< std::string > &subspaces) const |
| Get the set of subspaces that this space and other have in common. The computed list of subspaces does not contain spaces that cover each other, even though they may be common, as that is redundant information. | |
| virtual void | computeLocations () |
| Compute the location information for various components of the state space. Either this function or setup() must be called before any calls to getValueAddressAtName(), getValueAddressAtLocation() (and other functions where those are used). | |
Protected Attributes | |
| int | type_ |
| A type assigned for this state space. | |
| StateSamplerAllocator | ssa_ |
| An optional state sampler allocator. | |
| double | maxExtent_ |
| The extent of this space at the time setup() was called. | |
| double | longestValidSegmentFraction_ |
| The fraction of the longest valid segment. | |
| double | longestValidSegment_ |
| The longest valid segment at the time setup() was called. | |
| unsigned int | longestValidSegmentCountFactor_ |
| The factor to multiply the value returned by validSegmentCount(). Rarely used but useful for things like doubling the resolution. | |
| std::map< std::string, ProjectionEvaluatorPtr > | projections_ |
| List of available projections. | |
| ParamSet | params_ |
| The set of parameters for this space. | |
| std::vector< ValueLocation > | valueLocationsInOrder_ |
| The value locations for all varliables of type double contained in a state; The locations point to values in the same order as that returned by getValueAddressAtIndex() | |
| std::map< std::string, ValueLocation > | valueLocationsByName_ |
| All the known value locations, by name. The names of state spaces access the first element of a state. RealVectorStateSpace dimensions are used to access individual dimensions. | |
| std::map< std::string, SubstateLocation > | substateLocationsByName_ |
| All the known substat locations, by name. | |
Static Protected Attributes | |
| static const std::string | DEFAULT_PROJECTION_NAME = "" |
| The name used for the default projection. | |
Debugging tools | |
| virtual void | printState (const State *state, std::ostream &out=std::cout) const |
| Print a state to a stream. | |
| virtual void | printSettings (std::ostream &out) const |
| Print the settings for this state space to a stream. | |
| virtual void | printProjections (std::ostream &out) const |
| Print the list of registered projections. This function is also called by printSettings() | |
| virtual void | sanityChecks (double zero, double eps, unsigned int flags) const |
| Perform sanity checks for this state space. Throws an exception if failures are found. More... | |
| virtual void | sanityChecks () const |
| Convenience function that allows derived state spaces to choose which checks should pass (see SanityChecks flags) and how strict the checks are. This just calls sanityChecks() with some default arguments. | |
| void | diagram (std::ostream &out) const |
| Print a Graphviz digraph that represents the containment diagram for the state space. | |
| void | list (std::ostream &out) const |
| Print the list of all contained state space instances. | |
| static void | Diagram (std::ostream &out) |
| Print a Graphviz digraph that represents the containment diagram for all the instantiated state spaces. | |
| static void | List (std::ostream &out) |
| Print the list of available state space instances. | |
Detailed Description
Representation of a space in which planning can be performed. Topology specific sampling, interpolation and distance are defined.
See Implementing State Spaces.
Definition at line 134 of file StateSpace.h.
Member Enumeration Documentation
◆ SanityChecks
Flags to use in a bit mask for state space sanity checks. Some basic checks do not have flags associated (they are always executed; for example, whether copyState() works as expected)
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| STATESPACE_DISTANCE_DIFFERENT_STATES | Check whether the distances between non-equal states is strictly positive (StateSpace::distance()) |
| STATESPACE_DISTANCE_SYMMETRIC | Check whether the distance function is symmetric (StateSpace::distance()) |
| STATESPACE_INTERPOLATION | Check whether calling StateSpace::interpolate() works as expected. |
| STATESPACE_TRIANGLE_INEQUALITY | Check whether the triangle inequality holds when using StateSpace::interpolate() and StateSpace::distance() |
| STATESPACE_DISTANCE_BOUND | Check whether the StateSpace::distance() is bounded by StateSpace::getExtent() |
| STATESPACE_RESPECT_BOUNDS | Check whether sampled states are always within bounds. |
| STATESPACE_ENFORCE_BOUNDS_NO_OP | Check that enforceBounds() does not modify the contents of states that are within bounds. |
| STATESPACE_SERIALIZATION | Check whether the StateSpace::serialize() and StateSpace::deserialize() work as expected. |
Definition at line 198 of file StateSpace.h.
Member Function Documentation
◆ as() [1/2]
|
inline |
Cast this instance to a desired type.
Make sure the type we are casting to is indeed a state space
Definition at line 151 of file StateSpace.h.
◆ as() [2/2]
|
inline |
Cast this instance to a desired type.
Make sure the type we are casting to is indeed a state space
Definition at line 161 of file StateSpace.h.
◆ copyState()
|
pure virtual |
Copy a state to another. The memory of source and destination should NOT overlap.
- Note
- For more advanced state copying methods (partial copy, for example), see Advanced methods for copying states.
Implemented in ompl::base::CompoundStateSpace, ompl::base::WrapperStateSpace, ompl::base::RealVectorStateSpace, ompl::base::AtlasStateSpace, ompl::base::SO3StateSpace, ompl::base::TimeStateSpace, ompl::base::CForestStateSpaceWrapper, ompl::base::DiscreteStateSpace, and ompl::base::SO2StateSpace.
◆ getMaximumExtent()
|
pure virtual |
Get the maximum value a call to distance() can return (or an upper bound). For unbounded state spaces, this function can return infinity.
- Note
- Tight upper bounds are preferred because the value of the extent is used in the automatic computation of parameters for planning. If the bounds are less tight, the automatically computed parameters will be less useful.
Implemented in ompl::base::CompoundStateSpace, ompl::base::WrapperStateSpace, ompl::base::RealVectorStateSpace, ompl::base::SpaceTimeStateSpace, ompl::base::SO3StateSpace, ompl::base::EmptyStateSpace, ompl::base::CForestStateSpaceWrapper, ompl::base::DiscreteStateSpace, ompl::base::SO2StateSpace, and ompl::base::TimeStateSpace.
◆ getValueAddressAtIndex()
|
virtual |
Many states contain a number of double values. This function provides a means to get the memory address of a double value from state state located at position index. The first double value is returned for index = 0. If index is too large (does not point to any double values in the state), the return value is nullptr.
- Note
- This function does not map a state to an array of doubles. There may be components of a state that do not correspond to double values and they are 'invisible' to this function. Furthermore, this function is slow and is not intended for use in the implementation of planners. Ideally, state values should not be accessed by index. If accessing of individual state elements is however needed, getValueAddressAtLocation() provides a faster implementation.
Reimplemented in ompl::base::CompoundStateSpace, ompl::base::WrapperStateSpace, ompl::base::RealVectorStateSpace, ompl::base::SO3StateSpace, ompl::base::TimeStateSpace, ompl::base::SO2StateSpace, and ompl::base::CForestStateSpaceWrapper.
Definition at line 306 of file StateSpace.cpp.
◆ isDiscrete()
|
virtual |
Check if the set of states is discrete.
- Note
- In fact, because of limited numerical precision, the representation of all spaces is discrete; this function returns true if the corresponding mathematical object is a discrete one.
Reimplemented in ompl::base::WrapperStateSpace, ompl::base::DiscreteStateSpace, and ompl::base::CForestStateSpaceWrapper.
Definition at line 770 of file StateSpace.cpp.
◆ sanityChecks()
|
virtual |
Perform sanity checks for this state space. Throws an exception if failures are found.
- Note
- This checks if distances are always positive, whether the integration works as expected, etc.
Reimplemented in ompl::base::WrapperStateSpace, and ompl::base::CForestStateSpaceWrapper.
Definition at line 609 of file StateSpace.cpp.
◆ setLongestValidSegmentFraction()
|
virtual |
When performing discrete validation of motions, the length of the longest segment that does not require state validation needs to be specified. This function sets this length as a fraction of the space's maximum extent.
- Note
- This function's effect is not considered until after setup() has been called. For immediate effects (i.e., during planning) use setValidSegmentCountFactor()
Reimplemented in ompl::base::CompoundStateSpace, ompl::base::WrapperStateSpace, and ompl::base::CForestStateSpaceWrapper.
Definition at line 828 of file StateSpace.cpp.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- ompl/base/StateSpace.h
- ompl/base/src/StateSpace.cpp